
Solution
The Poker Test is the test for independence based on the frequency with which certain digits are repeated with in a series of numbers. This test not only tests for the randomness of the sequence of numbers, but also the digits comprising of each of the numbers. The expected value of each of the combination of digits in a number is compared with the observed value by means of the chi-square test for independence. The acceptance is done if the observed value of chi-square sums for all the possible combinations of digits is less than the acceptable value for the given degree of freedom at the specified confidence interval.
Poker test for four digit numbers
In four digit number, there are five different possibilities
All individual digits can be different
There can be one pair of like digit
There can be two pair of like digits
There can be three digits of a kind
There can be four digits of a kind
The probabilities associated with each of the possibilities is given by
P (four different digits) = 4C4 * (10/10) * (9/10) * (8/10) * (7/10) = 0.504
P (one pair) = 4C2 * (10/10) * (1/10) * (9/10) * (8/10) = 0.432
P (two pair) = (4C2/2)*(10/10) * (1/10) * (9/10) * (1/10) = 0.027
P (three digits of a kind) = 4C3 * (10/10) * (1/10) * (1/10) * (9/10) = 0.036
P (four digits of a kind) = 4C4 * (10/10) * (1/10) * (1/10) * (1/10) = 0.001
Now the calculation table for the Chi-square statistics is:
|
Combination(i) |
Observed Frequency(Oi) |
Expected Frequency(Ei) |
(Oi-Ei) |
(Oi-Ei)2/Ei |
|
Four different digits |
5120 |
0.504*10000 = 5040 |
80 |
1.269 |
|
One pair |
4230 |
0.432*10000 = 4320 |
-90 |
1.875 |
|
Two pair |
560 |
0.027*10000 = 270 |
290 |
311.481 |
|
Three digits of a kind |
75 |
0.036*10000 = 360 |
285 |
225.625 |
|
Four digits of a kind |
15 |
0.001*10000 = 10 |
5 |
2.5 |
|
10000 |
10000 |
Σ(Oi-Ei)2/Ei = 542.75 |
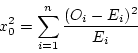 = 542.75
= 542.75
and Given X2a,N = X20.05,4 = 9.49
Here the calculated value of chi-square is 542.75 which is greater than the given tabulated value of chi- square so we reject the null hypothesis of independence between given numbers.
Ⓒ Copyright ESign Technology 2019. A Product of ESign Technology. All Rights Reserved.